-
-
Path Planning for Static Obstacle Avoidance of Autonomous Vehicles based on Imitation Learning and Optimization Technique
모방 학습 및 최적화 기법에 기반한 자율주행 차량의 고정 장애물 회피 경로 계획 연구
-
Youngmin Yoon, Jaewan Lee
윤영민, 이재완
- Imitation learning has been one of the mainstream methods for achieving autonomous driving in recent years. Despite its simple structure and expert-like …
- Imitation learning has been one of the mainstream methods for achieving autonomous driving in recent years. Despite its simple structure and expert-like performance in dealing with diverse driving situations, it may lead to unsafe driving solutions due to the absence of a constraint-checking process. To resolve this problem, this paper presents a method for path planning of autonomous vehicles based on imitation learning and optimization techniques. In this paper, imitation learning is used to derive the expert-like driving path. For this, a neural network is trained in a supervised manner to derive the driving path output given environmental information and a reference path. An optimization technique is applied to post-process the imitation-based driving path result using a cost function and constraints. This contributes to enhanced safety compared to a path planner based solely on imitation learning. The proposed algorithm has been validated via simulation studies. The test results show that the proposed combination of imitation learning and optimization techniques enables the autonomous vehicle to derive a feasible driving path following the expert driving pattern. The addition of the optimization technique is shown to reduce collision rate compared to the neural network-based path planning. - COLLAPSE
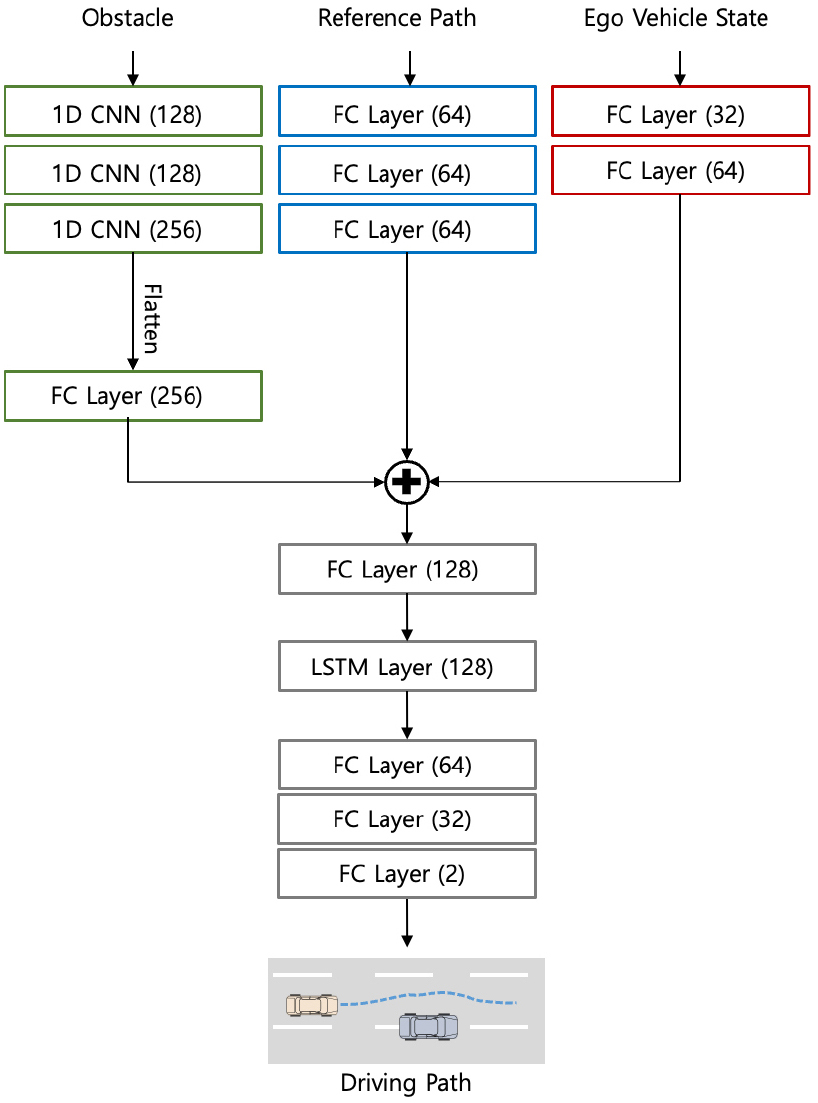
-
Path Planning for Static Obstacle Avoidance of Autonomous Vehicles based on Imitation Learning and Optimization Technique
-
-
A Study on the Introduction of Eco-Friendly Ground Support Equipment at Airport
우리나라 공항 친환경 지상조업장비 도입에 관한 연구
-
Deokho Kim
김덕호
- In accordance with trends in responding to the global climate crisis, goals are being established to achieve carbon neutrality in various fields. …
- In accordance with trends in responding to the global climate crisis, goals are being established to achieve carbon neutrality in various fields. One of these is a plan to convert diesel ground handling equipment at Korea's airports to eco-friendly. Currently, domestic airport ground handling companies are making efforts to convert existing diesel equipment to eco-friendly equipment, but are complaining of difficulties due to the lack of required technology and management plans. Accordingly, through research on ways to convert old diesel ground handling equipment at the airport into eco-friendly equipment, we would like to present data necessary to induce rapid eco-friendly conversion and realize the goal of carbon neutrality. - COLLAPSE
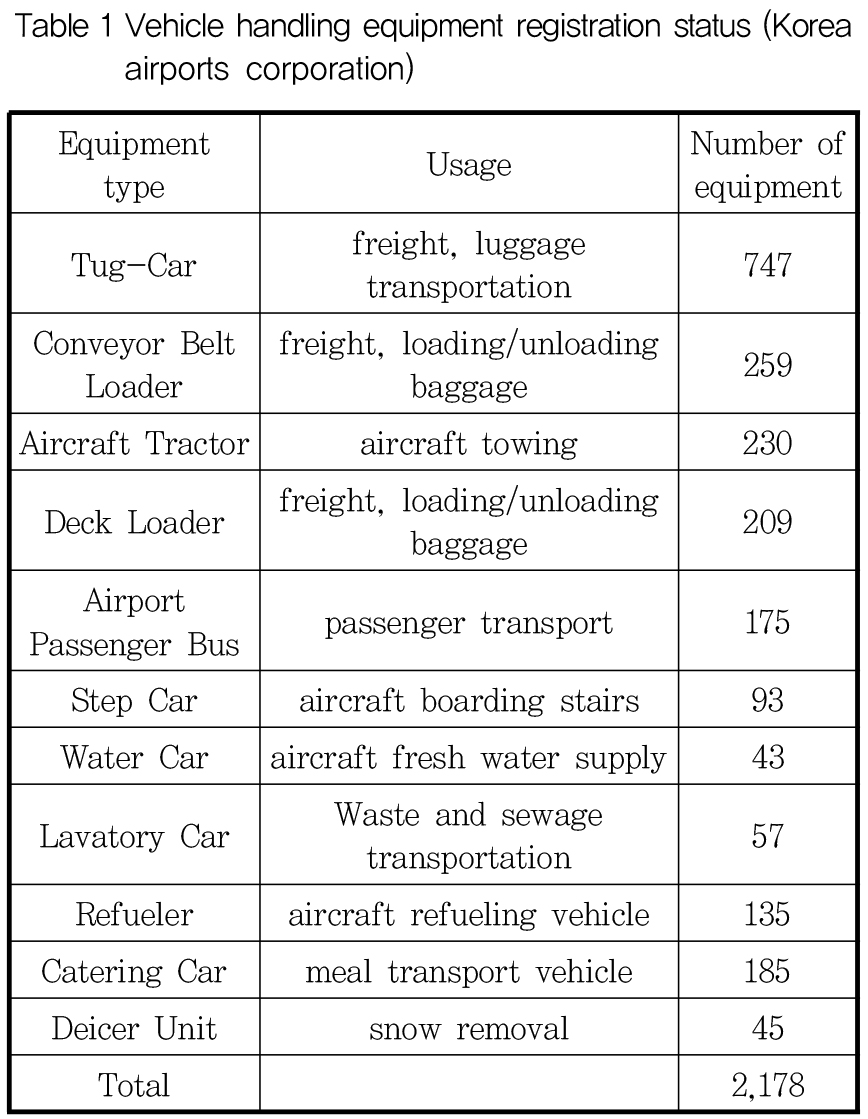
-
A Study on the Introduction of Eco-Friendly Ground Support Equipment at Airport
-
-
A Study on the Delvelopment of Platoon Autonomous Driving Scenarios Reflecting Video Data of Tire Departure Accidents
타이어 이탈 사고 영상데이터를 반영한 군집자율주행 시나리오 개발에 관한 연구
-
Yongsoon Choi, Kijung Park, Seungyoon Jung, Seryong Baek, Chonho Kim
최용순, 박기정, 정승윤, 백세룡, 김천호
- This study is a scenario in which actual tire departure accidents are reproduced using the PC-Crash program and reflected in platooning autonomous …
- This study is a scenario in which actual tire departure accidents are reproduced using the PC-Crash program and reflected in platooning autonomous vehicles. This is a scenario in which a platooning autonomous vehicle drives in the opposite lane as a scenario in which a tire leaves and goes to the opposite lane, causing the preceding vehicle to avoid the tire and collide with the following vehicle. As a result of applying the scenario, it was possible to check whether or not it was avoided according to the inter-vehicle distance from the preceding vehicle of platooning autonomous driving. In addition, it is expected that this scenario can be used as a platooning test scenario as it can check whether or not to avoid collision through V2X communication. - COLLAPSE
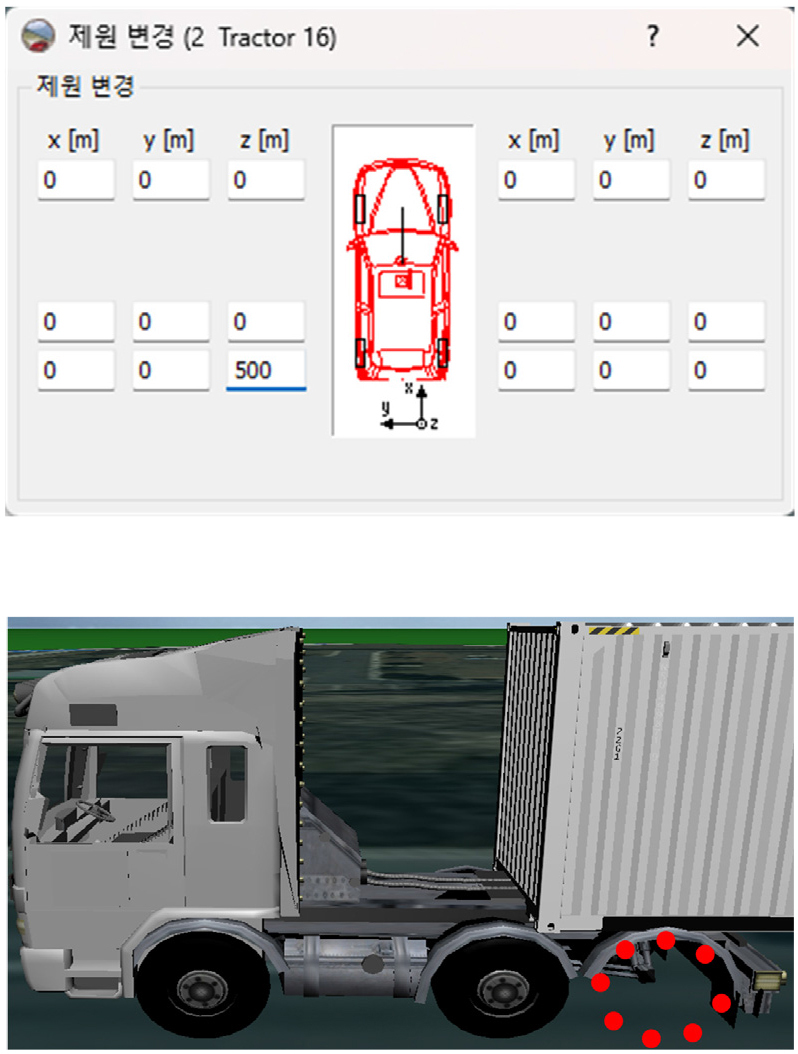
-
A Study on the Delvelopment of Platoon Autonomous Driving Scenarios Reflecting Video Data of Tire Departure Accidents
-
-
Implementation of Autonomous Driving HMI and Study on Sharp Turn Detection System for Vulnerable User
자율주행 차량의 교통약자 안전을 위한 급회전 검출 HMI 시스템
-
Su-in Park, Kyung-duck Seo, Jeong-kyu Bae, Dae-wha Seo
박수인, 서경덕, 배정규, 서대화
- This study proposes a Human-Machine Interface (HMI) implementation for autonomous vehicles aimed at ensuring the safety of vulnerable vehicle users, such as …
- This study proposes a Human-Machine Interface (HMI) implementation for autonomous vehicles aimed at ensuring the safety of vulnerable vehicle users, such as the elderly, disabled, and residents of transportation-disadvantaged areas. Particularly, sharp turn detection algorithm was developed to provide pre-emptive warnings to passengers about sudden vehicle movements, enhancing safety and comfort. Field tests conducted using high-definition map (HD map) of Sejong City demonstrated the effectiveness of the system, allowing autonomous vehicles to detect sharp turns in advance and display appropriate warning messages through the HMI. The results show that the proposed system improves the safety of vulnerable vehicle users by providing early detection of sharp turns, thus reducing potential risks during autonomous vehicle rides. This research highlights the importance of user-friendly and intuitive HMI systems for increasing public trust and acceptance of autonomous driving technologies, and it contributes to the development of a more inclusive and accessible transportation system. The findings are expected to play a key role in advancing the commercialization and widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles for all users. - COLLAPSE
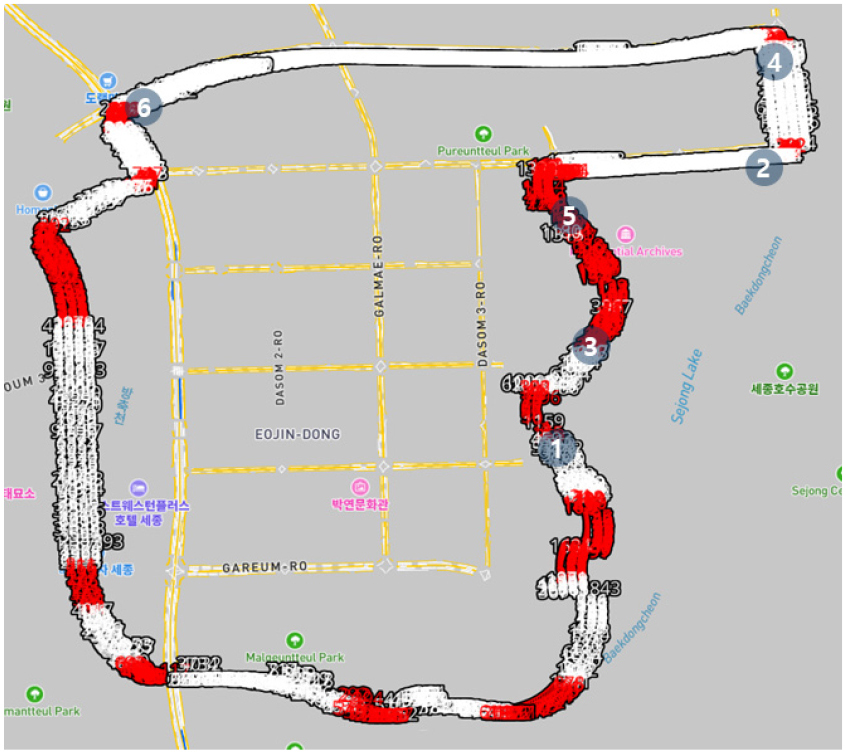
-
Implementation of Autonomous Driving HMI and Study on Sharp Turn Detection System for Vulnerable User
-
-
A Study on Criteria for the In-Vehicle Installation of V2X System Units
V2X 시스템 단위 장치의 차량 장착 기준에 관한 연구
-
Yoowon Kim
김유원
- According to the government's plan to complete the foundation for the commercialization of convergence level 4+ autonomous vehicles in 2027, the V2X …
- According to the government's plan to complete the foundation for the commercialization of convergence level 4+ autonomous vehicles in 2027, the V2X system is expected to become basic equipment in vehicles. The V2X system broadcasts various status information, including location data, to the surrounding environment in real time. Therefore, the legal basis and installation criteria need to be established first. Based on standards, laws, administrative regulations and previous research results related to V2X system, a draft of V2X system installation standards has been derived. The draft of the Vehicle Management Act, the draft of the Enforcement Rules of the Vehicle Management Act and the draft of the Regulation on Performance and Standards of Vehicles and Vehicle Parts in relation to the installation criteria of V2X system have been studied, revised and supplemented. We believe that the draft of the installation criteria for V2X systems for the fusion of autonomous driving and C-ITS will provide a legal basis. - COLLAPSE
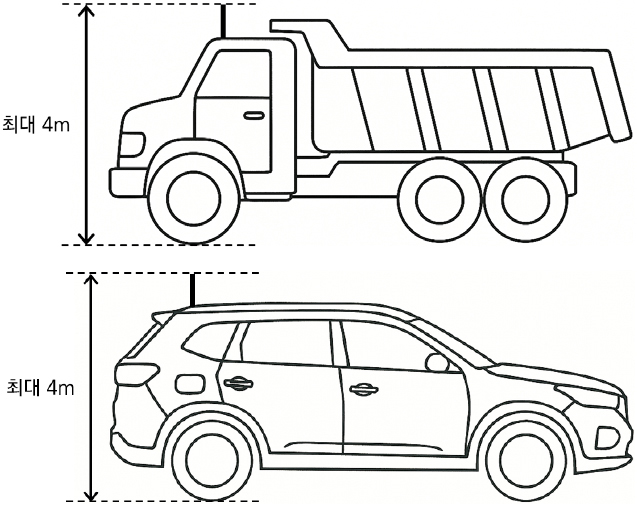
-
A Study on Criteria for the In-Vehicle Installation of V2X System Units
-
-
A Study on the Effect of Friction Coefficient in Vehicle FE Model for Virtual Crash Test Results
유한요소모델의 마찰계수가 충돌해석결과에 미치는 영향 연구
-
Kyungjin Kim, Jaeho Shin, Siwoo Kim
김경진, 신재호, 김시우
- The essential process of automobile crash testing, which evaluates the collision safety and occupant protection performance of vehicles, is costly. As a …
- The essential process of automobile crash testing, which evaluates the collision safety and occupant protection performance of vehicles, is costly. As a result, virtual crash testing, which can substitute or complement real-world testing, is being researched and applied as an effective alternative. As the application scope of virtual crash testing expands, research is actively being conducted to verify the reliability of the results obtained from virtual crash tests and their similarity to real-world crash tests. In this study, the effect of changing the coefficient of friction between the passenger and vehicle contact parts during high-speed collisions in a specific range of friction coefficients was quantitatively analyzed. It was found that the impact of the friction coefficient varied depending on the analysis model, and in the crash analysis, there were differences in the maximum reaction force and the shape of the reaction force curve over time. Therefore, it is necessary to examine the range of friction coefficients applicable to virtual crash testing. - COLLAPSE
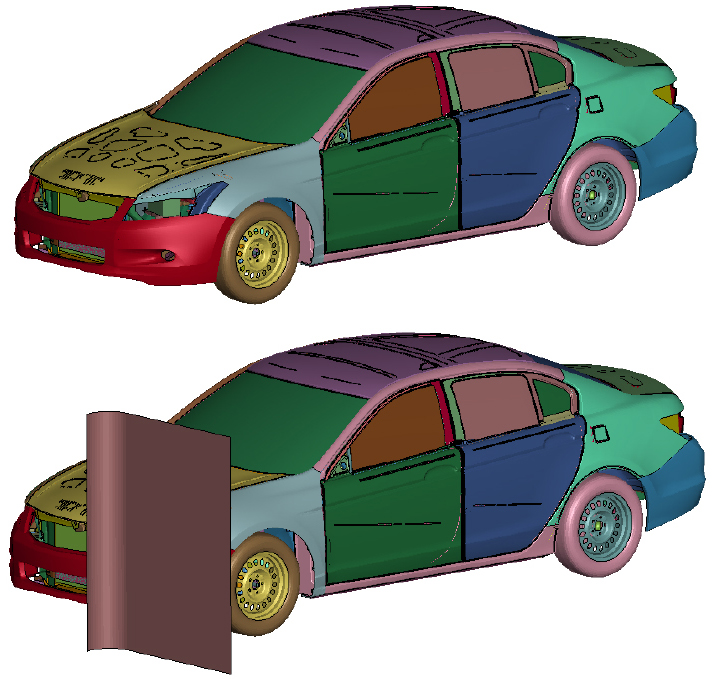
-
A Study on the Effect of Friction Coefficient in Vehicle FE Model for Virtual Crash Test Results
-
-
A Comparative Study on Technology Management and Economic Innovation between Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
전기차와 수소전기차의 기술경영 전략 및 경제 혁신 비교 연구
-
Junseok Lee, Hokyung Kim, Taeseok Oh
이준석, 김호경, 오태석
- The global response to the climate crisis and the ongoing energy transition are driving a rapid restructuring of industrial systems worldwide. In …
- The global response to the climate crisis and the ongoing energy transition are driving a rapid restructuring of industrial systems worldwide. In the transportation sector, Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCEVs) are emerging as central technologies for achieving carbon neutrality and sustainable mobility. This study conducts a comparative analysis of BEVs and FCEVs from the perspectives of technology management and economic innovation. It further examines domestic and international policy responses and industrial strategies to assess the competitiveness and sustainability of each technology. Based on the findings, this paper offers strategic insights for securing competitive advantage in the global eco-friendly vehicle market. - COLLAPSE
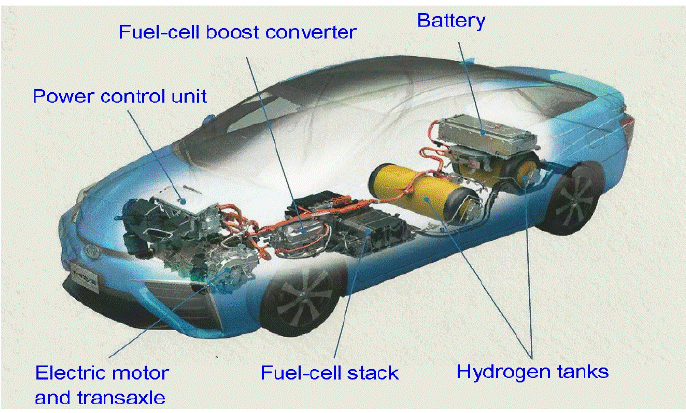
-
A Comparative Study on Technology Management and Economic Innovation between Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
-
-
Motion Sickness-Energy Efficiency Correlation Analysis by Regenerative Braking System Mode of Electric Vehicles Considering PMSM Efficiency Map
PMSM 효율맵을 고려한 전기차의 회생제동 시스템 모드별 멀미-에너지 효율 상관관계 분석
-
Buseong Kim, Chunhwan Lee
김부성, 이천환
- This paper analyzes the relation between energy efficiency and motion sickness in electric vehicles (EVs) under different regenerative braking modes. Simulations were …
- This paper analyzes the relation between energy efficiency and motion sickness in electric vehicles (EVs) under different regenerative braking modes. Simulations were conducted on the FTP-75 cycle with varying braking levels. Energy consumption was evaluated, and motion sickness was measured using the ISO 2631-1 based Motion Sickness Dose Value (MSDV). Results revealed a trade-off, as higher braking levels improved energy recovery but also increased motion sickness. This quantitative analysis provides meaningful insights into the trade-off between energy efficiency and motion sickness, offering a valuable basis for future EV design and evaluation. - COLLAPSE
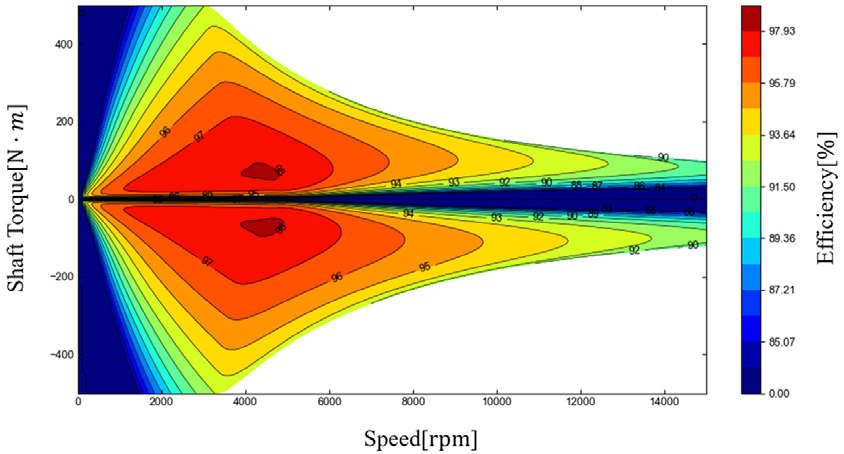
-
Motion Sickness-Energy Efficiency Correlation Analysis by Regenerative Braking System Mode of Electric Vehicles Considering PMSM Efficiency Map
-
-
A Study on KADAS Compatibility with Diverse ADAS Camera Sensor Architectures
다양한 ADAS 카메라 센서 아키텍처에 대한 KADAS 호환성 연구
-
Jiyang Park, Seongjae Ko, Jaehwan Jeong, Jinho Yang, Byeongil Kim, Changhwan Choi, Haeden Lee, Jongwoo Park
박지양, 고성재, 정재환, 양진호, 김병일, 최창환, 이해든, 박종우
- This study investigates the compatibility of the KADAS (Korea Automated Driving Vehicle Assessment System) - Based Vehicle in the Loop Simulation (VILS) …
- This study investigates the compatibility of the KADAS (Korea Automated Driving Vehicle Assessment System) - Based Vehicle in the Loop Simulation (VILS) environment with diverse ADAS Camera sensor architectures. Specifically, it analyzes the functional performance of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) for Vehicle A, equipped with a mono-camera system, and Vehicle B, utilizing a Stereo/Dual-camera system. The findings reveal that Vehicle A demonstrated high success rates in Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB) functions. In contrast, Vehicle B exhibited Severe performance degradation in the same VILS environment. This degradation is attributed to the VILS environment’s inherent limitations in supporting the depth perception mechanisms of stereo/dual cameras and the conservative nature of their sensor fusion logic. This research underscores the critical need for improving ADAS evaluation technologies within VILS environments to accommodate various sensor architectures, thereby contributing essential foundational data for standardized ADAS performance assessment. - COLLAPSE
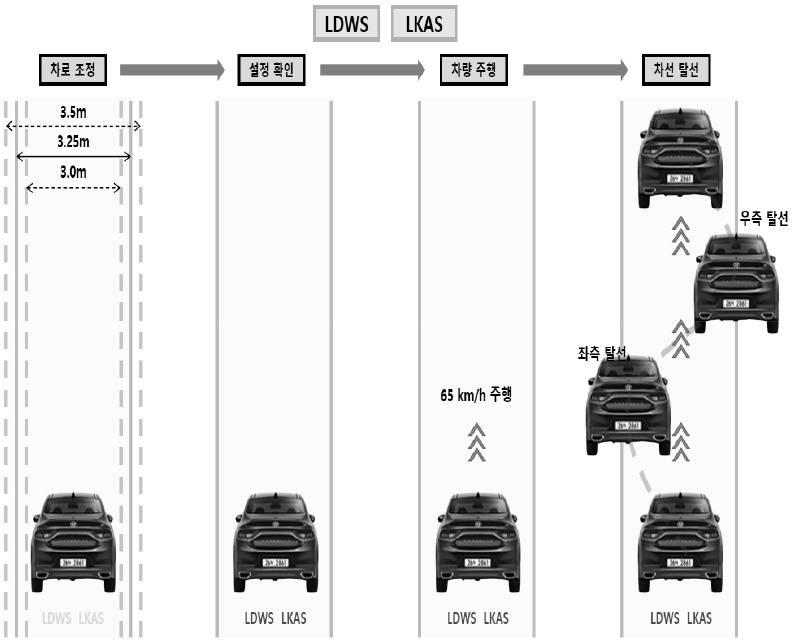
-
A Study on KADAS Compatibility with Diverse ADAS Camera Sensor Architectures
-
-
A Study on the Development of V2X Communication Performance and Safety Evaluation Technology for Vehicles in a Congested V2X Communication Environment
V2X 통신 혼잡 환경에서의 자동차 V2X 통신성능 안전성 평가기술 개발에 관한 연구
-
Seonkeon Kim, Hyungjin Kim, Hyesoo Kim
김선건, 김형진, 김혜수
- V2X communication technology can overcome the limitations of existing Lv. 3 autonomous vehicles by recognizing surrounding traffic conditions and road hazards beyond …
- V2X communication technology can overcome the limitations of existing Lv. 3 autonomous vehicles by recognizing surrounding traffic conditions and road hazards beyond the recognition range of ADAS sensors, and its necessity is gradually increasing as a key technology for implementing Lv. 4 or higher autonomous driving. Major countries around the world (Europe, China, Japan), including Korea, are paying attention to accident prevention safety using V2X technology and have established a roadmap for the New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) and are introducing V2X technology as an NCAP evaluation item. In this study, we conducted research on the development of vehicle V2X communication performance safety evaluation technology, including evaluation items, evaluation environment, and evaluation method for evaluating the performance of congestion control technology of V2X communication devices installed in vehicles in an environment where V2X technology is applied to actual roads and numerous vehicles and infrastructures communicate simultaneously, resulting in communication congestion and V2X communication performance degradation. - COLLAPSE
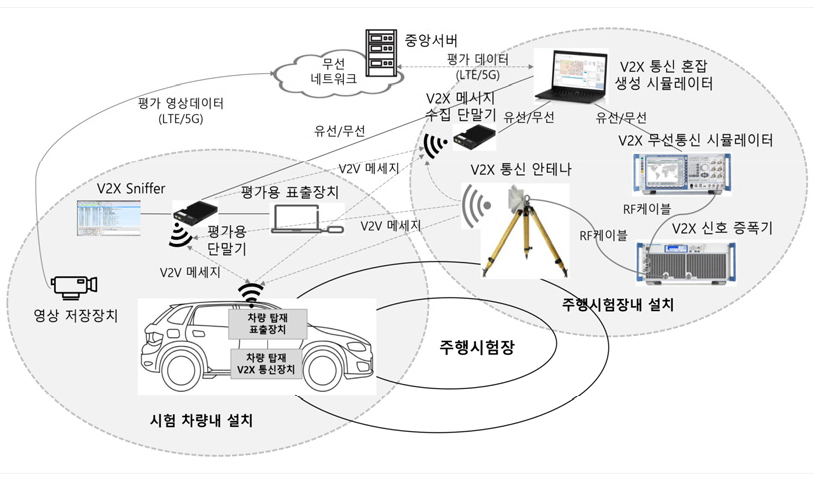
-
A Study on the Development of V2X Communication Performance and Safety Evaluation Technology for Vehicles in a Congested V2X Communication Environment
-
-
Analysis of Electric Vehicle Fire Characteristics Through Statistical Methods
통계적 기법을 통한 전기자동차 화재 특성 연구
-
Hee sung Yun
윤희성
- This study investigates the structural characteristics and underlying risk factors of electric vehicle (EV) fires through a statistical analysis of 148 documented …
- This study investigates the structural characteristics and underlying risk factors of electric vehicle (EV) fires through a statistical analysis of 148 documented cases in South Korea between 2018 and 2024. While public concern regarding EV fire safety has intensified alongside the rapid adoption of electric vehicles, empirical and data-driven research remains limited in the South Korean context. To address this gap, the study employs a suite of multivariate statistical techniques—including descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, binary logistic regression, and hierarchical cluster analysis—to examine fire occurrence patterns and risk profiles. The analysis reveals statistically significant associations among battery manufacturer, operational status at the time of ignition, and the initial ignition source. By statistically validating domestic EV fire data, this study provides evidence-based insights into fire causation mechanisms and proposes targeted technical improvements and policy recommendations to enhance electric vehicle safety. - COLLAPSE
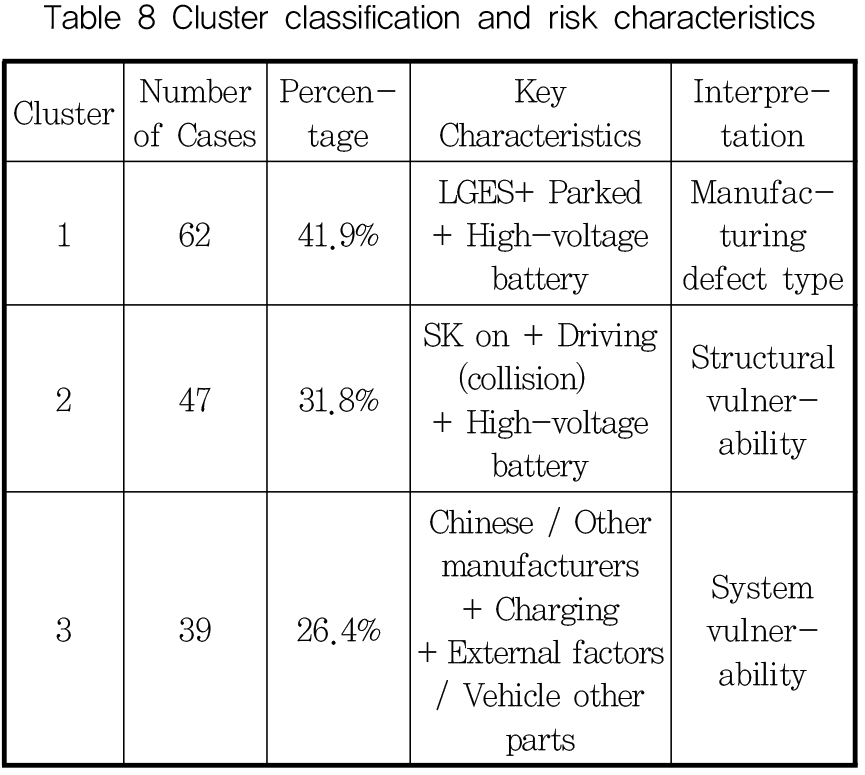
-
Analysis of Electric Vehicle Fire Characteristics Through Statistical Methods
-
-
Evaluation of Structural Safety According to Subframe Design and Mounting Method in EV-Converted Light Trucks
EV 개조가 적용된 소형 트럭의 서브프레임 형상과 장착 방법에 따른 구조 안전성 평가
-
Jinsuk Park, Jaewoong Lee, Sungyong Ha
박진석, 이재웅, 하성용
- This study was conducted in response to the CCPI 2025 report, which ranked South Korea among the lowest countries in greenhouse gas …
- This study was conducted in response to the CCPI 2025 report, which ranked South Korea among the lowest countries in greenhouse gas reduction performance, underscoring the need for more robust environmental policies. In particular, research efforts have intensified to address the slowdown in emission reduction within the transportation sector. This study analyzes the structural safety degradation of the main frame caused by the heavy battery used in EV-converted vehicles and proposes an improved subframe mounting method to extend the operational lifespan of such converted vehicles. Although conventional L-shaped brackets offer easy installation and low cost, they pose potential safety risks during long-term operation after conversion. Therefore, a refined subframe cross-sectional design was developed to distribute loads concentrated on the main frame, thereby reducing fatigue deformation and structural failure. The installed subframe was analyzed under three joint conditions—welded, bolted, and hybrid (weld-bolt combined)—to evaluate structural safety. Based on the comparative structural analysis results, the study presents an optimized subframe mounting method suitable for EV-converted light trucks. - COLLAPSE

-
Evaluation of Structural Safety According to Subframe Design and Mounting Method in EV-Converted Light Trucks
-
-
Development of Electric Vehicle Battery SOH Prediction Model using Vehicle Inspection Data
자동차검사 데이터를 활용한 전기자동차 배터리 상태지수 예측 모델 개발
-
Jungsoo Park, Youngmin Jang, Sein Oh, Hyunwoo Jo, Wonduck Park, Hosang Lee, Do-Gyeong Kim
박정수, 장영민, 오세인, 조현우, 박원덕, 이호상, 김도경
- This study develops an SOH prediction model for electric vehicle batteries using periodic technical inspection data collected under driving conditions. As the …
- This study develops an SOH prediction model for electric vehicle batteries using periodic technical inspection data collected under driving conditions. As the EV market expands rapidly, accurate SOH estimation is essential for battery safety management, maintenance optimization, and circular economy policy design. The model employs Ridge regression with L2 regularization to address multicollinearity among key predictors as vehicle age, cumulative mileage, total operating time, and total discharge. Cross-validation results showed MAE=2.24%p and RMSE=2.74%p, outperforming a random forest baseline. Variable importance analysis revealed that age and mileage were the strongest predictors, with calendar aging and cycle aging contributing comparably to SOH degradation. A framework is proposed to estimate time-to-threshold for SOH criteria using daily usage patterns. This supports targeted inspection scheduling, residual value assessment for used EVs, and policy development for battery reuse and recycling. By leveraging large-scale field inspection data, the research bridges the gap between laboratory-based SOH modeling and practical diagnostic applications for EV safety management. - COLLAPSE
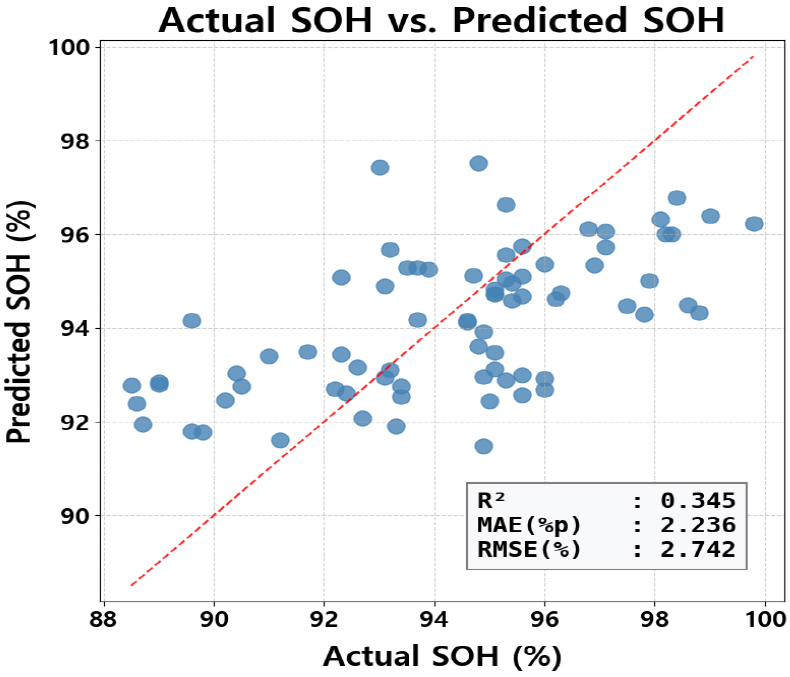
-
Development of Electric Vehicle Battery SOH Prediction Model using Vehicle Inspection Data
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Auto-vehicle Safety Association
Journal of Auto-vehicle Safety Association
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Auto-vehicle Safety Association
Journal of Auto-vehicle Safety Association









